Ion Channels
Reflecting work in the
The design of peptides that assemble in membranes to form functional ion channels is challenging. Specifically, hydrophobic interactions must be designed between the peptides and at the peptide–lipid interfaces simultaneously.
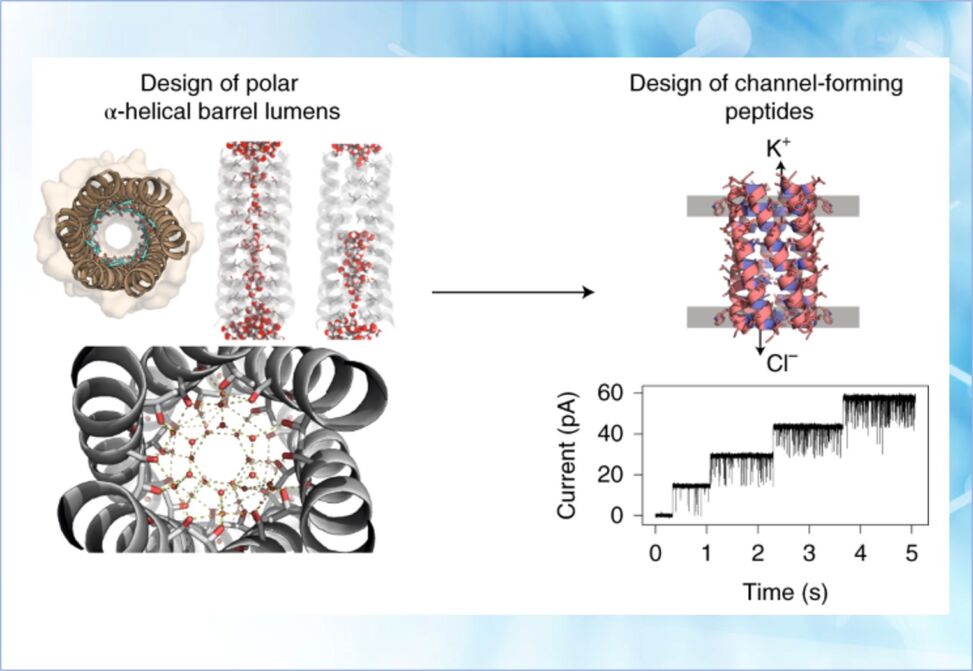
Herein is described a multi-step approach towards this problem. First, the researchers used rational de novo design to generate water-soluble α-helical barrels with polar interiors, and confirm their structures using high-resolution X-ray crystallography. These α-helical barrels have water-filled lumens like those of transmembrane channels.
Next, they modified the sequences to facilitate their insertion into lipid bilayers. Single-channel electrical recordings and fluorescent imaging of the peptides in membranes show monodisperse, cation-selective channels of unitary conductance.
Surprisingly, however, an X-ray structure solved from the lipidic cubic phase for one peptide reveals an alternative state with tightly packed helices and a constricted channel. To reconcile these observations, they performed computational analyses to compare the properties of possible different states of the peptide.