Self-Healable Composites
Reflecting recent work in the Pal and Balakrishnan Labs
Extracellular matrix, ECM, elasticity remains a crucial parameter to determine cell–material interactions, namely adhesion, growth, and differentiation, cellular communication, and migration that are essential to tissue repair and regeneration. Supramolecular peptide hydrogels with their 3-dimensional porous network and tuneable mechanical properties have emerged as an excellent class of ECM-mimetic biomaterials with relevant dynamic attributes and bioactivity.

The Pal Group
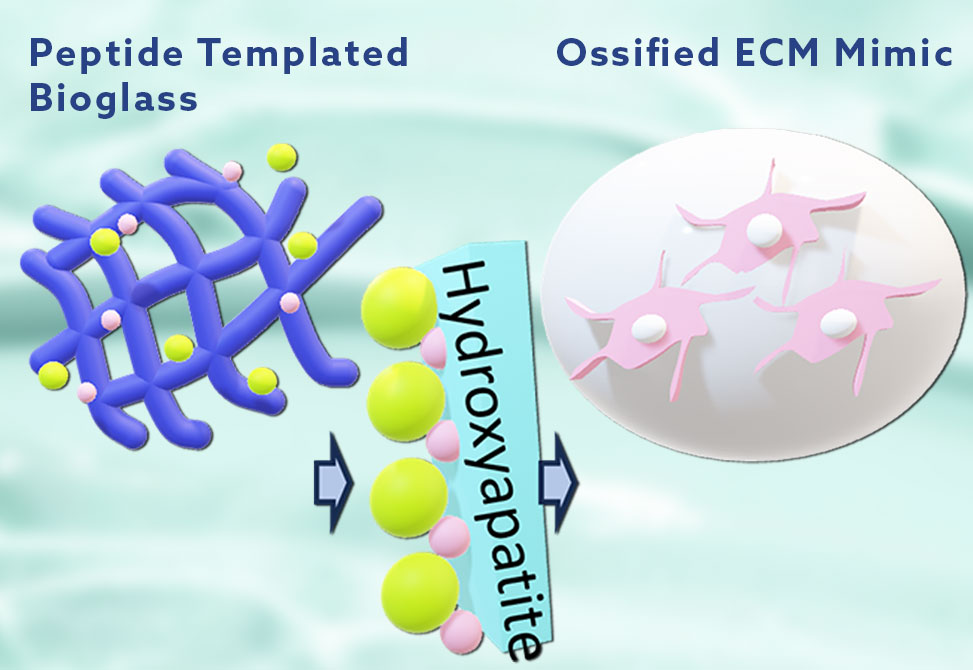
In work published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B, researchers from the Pal and Balakrishnan labs from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology, Mohali, and Indian Institute of Technology, Mandi, demonstrate the design of minimalist amyloid-inspired peptide amphiphiles, CnPA (n = 6, 8, 10, 12) with tuneable peptide nanostructures that are efficiently biomineralized and cross-linked using bioactive silicates.
Such hydrogel composites, CnBG exhibit excellent mechanical attributes and possess excellent self-healing abilities and collagen-like strain-stiffening ability as desired for bone ECM mimetic scaffold. The composites exhibited the formation of a hydroxyapatite mineral phase upon incubation in a simulated body fluid that rendered mechanical stiffness akin to the hydroxyapatite-bridged collagen fibers to match the bone tissue elasticity eventually. In a nutshell, peptide nanostructure-guided temporal effects and mechanical attributes demonstrate C8BG to be an optimal composite.
Finally, such constructs feature the potential for adhesion, proliferation of U2OS cells, high alkaline phosphatase activity, and osteoconductivity.