Automated Peptide Synthesis
Getting Started with Automated Peptide Synthesis
Peptide synthesis, an integral component of life sciences and drug discovery, has undergone a remarkable evolution. The routine use of automated peptide synthesizers has elevated the efficiency and reproducibility of this once labor-intensive process. This article will explore the fundamentals of automated peptide synthesis, its associated principles, and the innovative technologies that have revolutionized modern workflows.
Understanding Automated Peptide Synthesis
Automated peptide synthesis utilizes robotic systems and chemically robust protocols to streamline peptide production. This approach builds upon the foundation of Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis, SPPS, a groundbreaking technology introduced by Bruce Merrifield. SPPS enables the stepwise construction of peptides anchored to a solid substrate, facilitating easy removal of unreacted reagents.
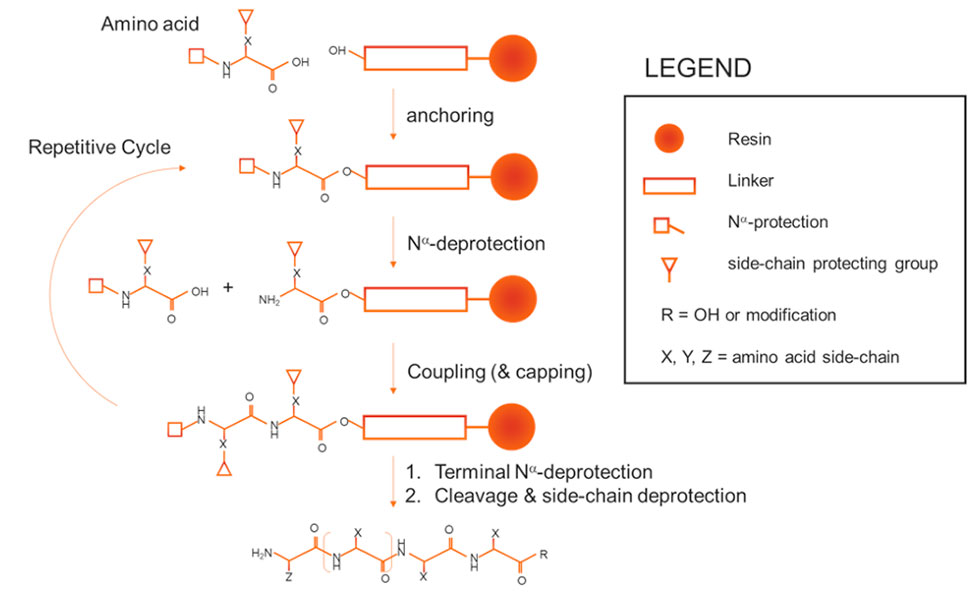
Figure 1: Reaction scheme for solid-phase peptide synthesis, SPPS
Core Principles and Benefits of Automation
Automation of SPPS has transformed peptide science by standardizing the deprotection, coupling, and washing steps into precise, repeatable cycles. This ensures reliable outcomes, minimal human error, and time savings while supporting parallel synthesis for high-throughput applications.
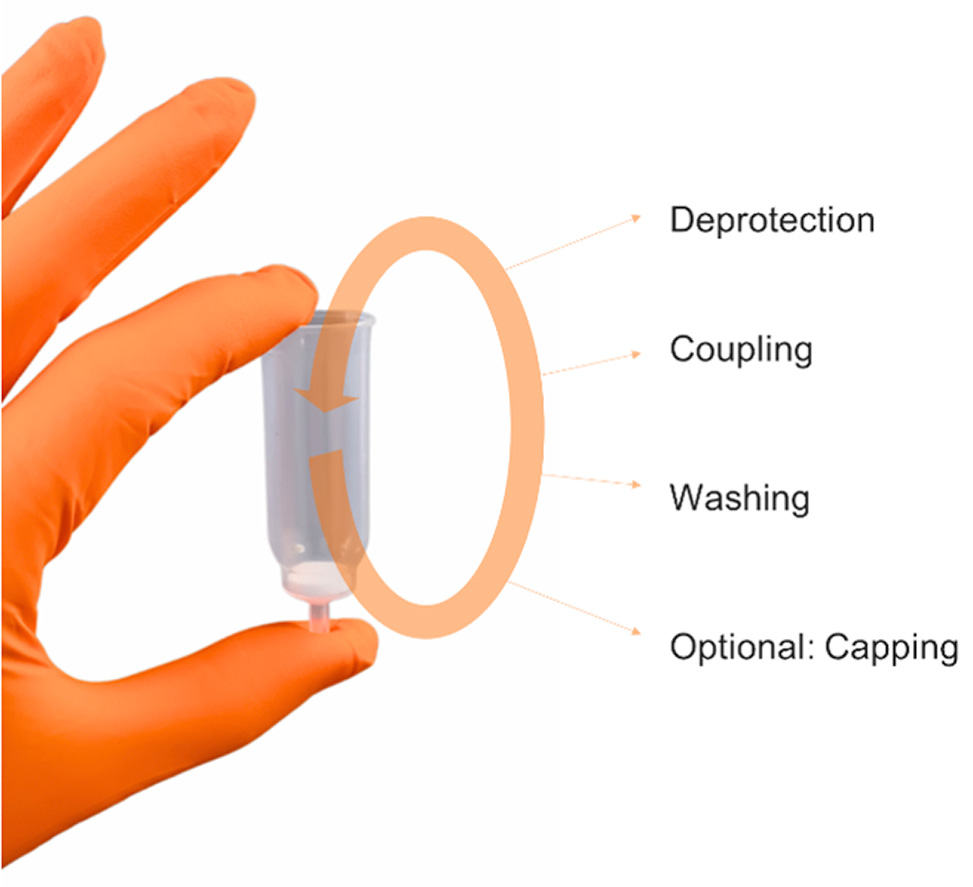
Figure 2: Basic automated steps during SPPS
The benefits of automation are vast:
Reduction of Manual Labor: High-tech systems require minimal human intervention, freeing researchers for other essential tasks.
Walk-Away Operations: Once configured, automated synthesizers can continuously operate without supervision.
Reproducibility: Automation eliminates variability across synthesis runs and users.
Parallel Processing: Allows multiple syntheses to occur simultaneously, thereby increasing throughput.
Components Enhancing Automation Success
Three core pillars are essential for successful synthesis automation:
![]() 1. SYSTEM
1. SYSTEM
The sophistication of modern systems stems from precise fluid handling, specialized reaction vessels, and application-specific features such as microfluidics and temperature control. System robustness is vital for enduring high-performance standards and long-term use.
![]() 2. SOFTWARE
2. SOFTWARE
Software functionality extends beyond hardware control. Advanced interfaces enable real-time monitoring, smart protocol customization, safety checks, and predictive alerts. These features optimize reaction conditions and safeguard synthesis integrity.
![]() 3. SERVICE
3. SERVICE
Expert guidance and comprehensive maintenance plans ensure long-term system optimization. Dedicated service support aids in initial setup, troubleshooting, and ongoing upgrades, enabling users to maximize their instrument's potential.
Role of Fluidic Design in Automation
Fluidic design directly impacts system reliability and synthesis quality. Minimizing dead volume and employing chemically inert components reduce reagent waste and prevent cross-contamination. Precise microfluidic channels ensure the accurate delivery of each reagent, making fluidic design a critical aspect of optimizing automation.
Video 1: Liquid handling using the PurePep® Pathway technology with a microfluidic valve block design.
Furthermore, high material resistance with chemically inert components endures harsh reagents and conditions, ensuring a long system lifetime.
Heating Capabilities
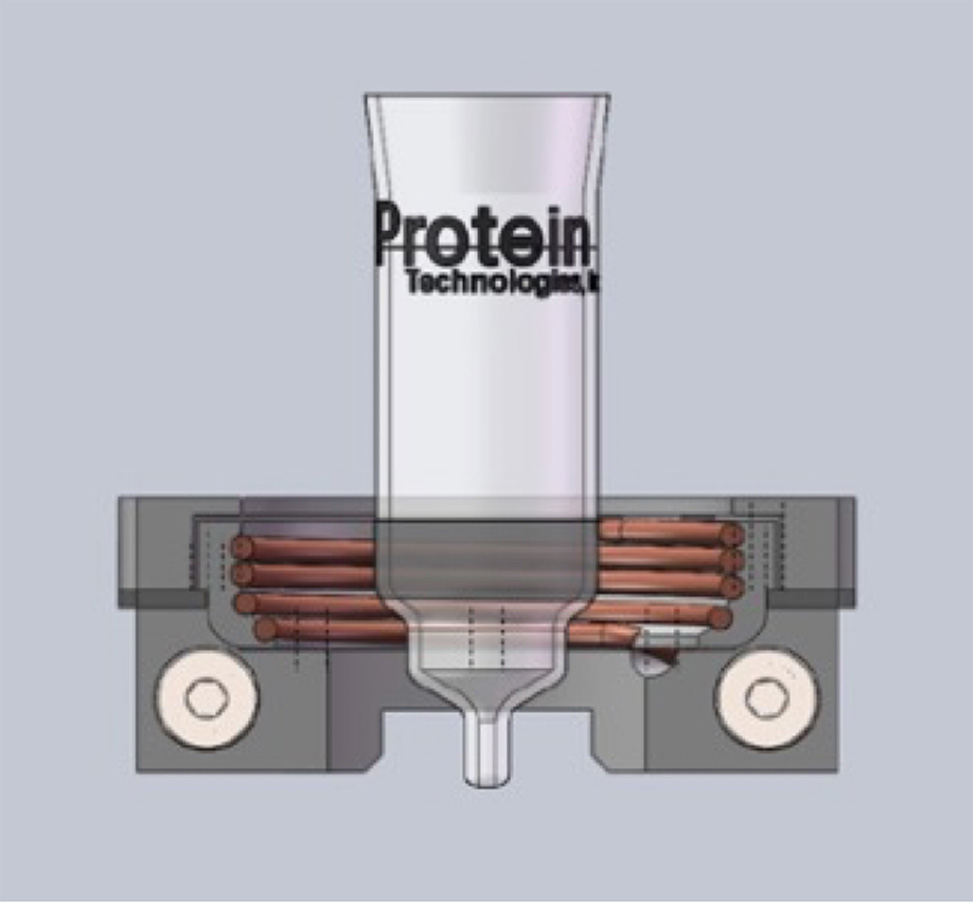
Figure 3: Induction Heating with PurePep® Chorus
Automated peptide synthesizers incorporate diverse heating capabilities, such as induction heating, see Figure 3, to address specific synthesis requirements. Enhanced temperature control enables accelerated coupling reactions, which is particularly beneficial for difficult sequences with sterically hindered residues. The integration of programmable heating cycles with synthesis protocols allows for customized thermal profiles optimized for specific amino acid combinations, significantly improving overall yield and purity. See table 1, below.
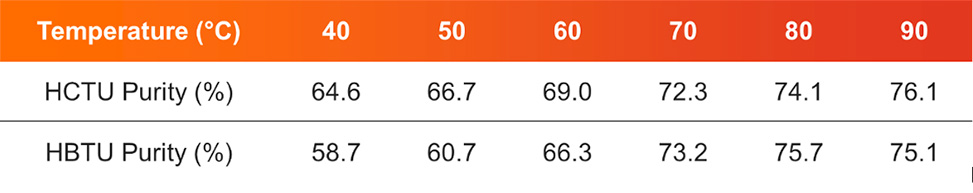
Table 1: Purity increases upon heating couplings with induction-heating in the PurePep® Chorus for ACP 65-74 synthesis
Integration of Advanced Features
Innovations like real-time UV monitoring enable users to track critical reaction parameters, ensuring the highest quality outcomes. Additional features like integrated purification and automated cleavage tools integrate seamlessly into workflows, reducing manual intervention.
Software for Enhanced Monitoring and Protocol Management
Automated synthesizers excel due to their advanced software capabilities, Figure 4. These include:
Protocol Management: Generate complex synthesis protocols tailored to project-specific needs.
Resource Optimization: Smart calculations ensure efficient use of reagents and reduce costs.
Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously track reaction progress remotely and receive critical alerts.
User Security: Enhanced record-keeping ensures compliance with industry regulations, facilitating data integrity across all synthesis steps.
Innovation Ready: The software's capabilities to flexibly control the movement of reagents and solvents allow novel chemistry automation, for example, with new green synthesis protocols or synthesis beyond peptides, such as oligonucleotides, peptide-nucleic acids, peptoids, foldamers, et cetera.
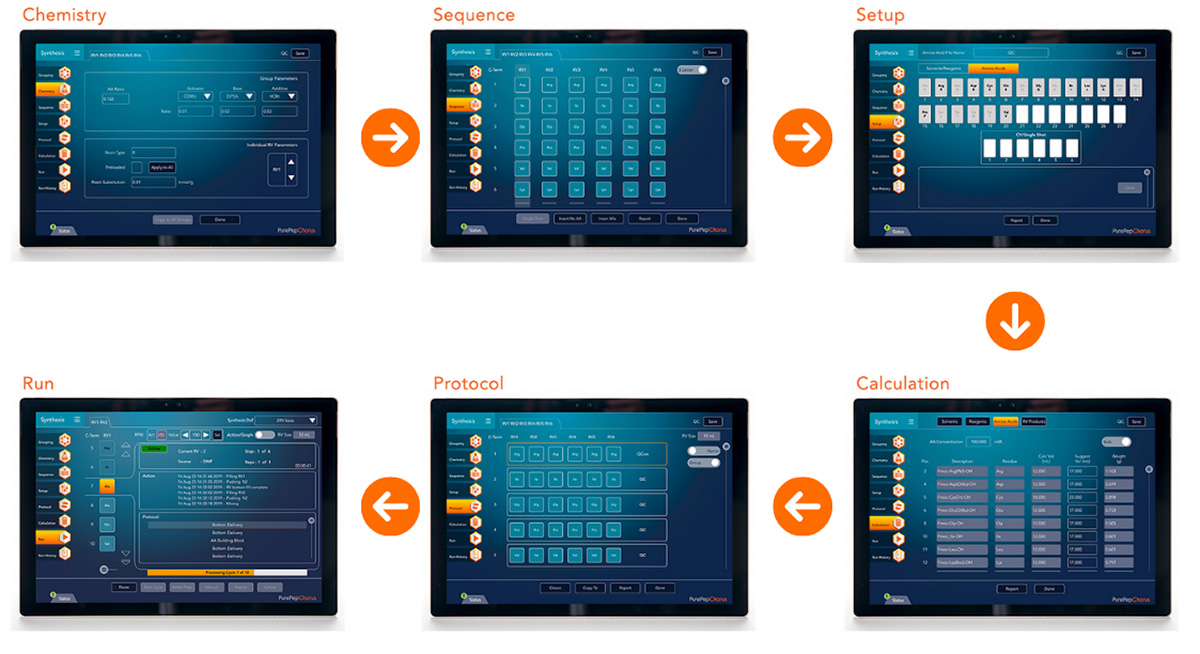
Figure 4: Protocol Management with the PurePep Software with advanced control capabilities and compliance features.
Scaling Capabilities
Different automated platforms cater to diverse operational needs, ranging from flexible, small-scale research setups to high-volume industrial production systems. Research-focused systems prioritize smaller reaction vessels and enhanced flexibility, whereas production-scale platforms offer scalability combined with streamlined workflows, see Figure 5.

Figure 5: Scalable reaction vessel configuration and additional features to meet research and production demands.

Designing a Synthesis
Advanced peptide synthesis requires precise input variables to ensure high-quality results. Developing a synthesis design involves detailed consideration of materials, process optimization, and systematic troubleshooting.
Key Steps in Designing a Synthesis
Successful peptide synthesis begins with choosing appropriate reagents and optimizing reaction conditions. The following components are foundational:
Starting Materials
Select the appropriate resin based on sequence complexity and production scale.
Choose a linker that suits your desired peptide’s functional group and cleavage process.
Evaluate resin swelling behavior to determine solvent requirements and reaction volume.
Optimizing Fmoc Deprotection:
Use the UV monitoring system to verify reaction completion in real-time.
Maintain appropriate reaction temperatures to prevent side reactions such as aspartimide formation—known for reducing crude purity.
Coupling Strategies:
Adjust reagent stoichiometry and excess to drive coupling efficiency based on peptide length and difficulty.
Implement heating solutions to accelerate coupling while preserving crude purity.
Take Your Skills Further
Watch the full Gyros Protein Technologies webinar on automated peptide synthesis to explore these principles and obtain more insights on overcoming synthesis challenges. Attendees gain access to advanced strategies, troubleshooting tips, and customizable system features to improve outcomes and increase efficiency.
Get free access to the webinar and transform your theoretical knowledge into hands-on expertise now!


