Stapled Peptides
Reflecting recent work in the
Diabetes is characterized by pancreas dysfunction and is commonly associated with obesity. Hypoglycemic agents capable of improving β-cell function and reducing body weight therefore are gaining increasing interest.
Though glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R)/cholecystokinin 2 receptor (CCK-2R) dual agonist ZP3022 potently increases β-cell mass and improves glycemic control in diabetic db/db mice, the in vivo half-life (t1/2) is short, and its body weight reducing activity is limited.
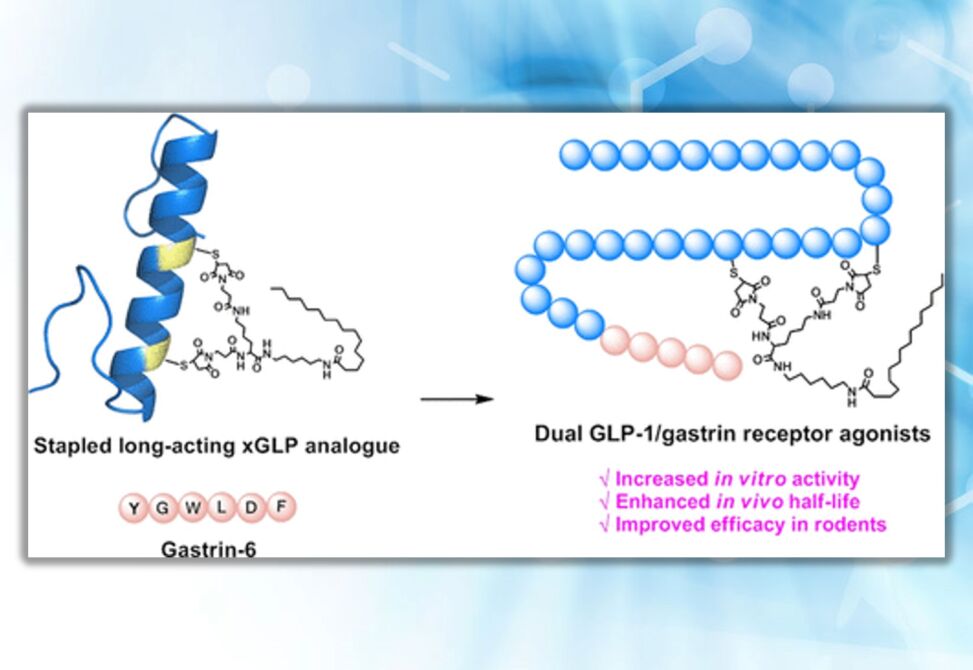
Herein is reported the discovery of a series of novel GLP-1R/CCK-2R dual agonists. Starting from Xenopus GLP-1, dual cysteine mutation was conducted followed by covalent side chain stapling and albumin binder incorporation, resulting in a stabilized secondary structure, increased agonist potency, and improved stability.
Further C-terminal conjugation of gastrin-6 generated GLP-1R/CCK-2R dual agonists, among which 6a and 6b showed higher stability and hypoglycemic activity than liraglutide and ZP3022. Desirably, 6a and 6b exhibited prominent metabolic benefits in diet-induced obesity mice without causing nausea responses and exerted considerable effects on β-cell restoration in db/db mice.
These preclinical studies suggest the potential role of GLP-1R/CCK-2R dual agonists as effective agents for treating diabetes and related metabolic disorders.